Discover and read the best of Twitter Threads about #Supplement
Most recents (18)
The findings of this one in mice suggest that dietary nitrate is capable of preserving mitochondrial bioenergetics during skeletal muscle disuse, and maintain mitochondrial-specific function during short-term (but not long-term) limb immobilization. 

- Skeletal muscle disuse reduces muscle protein synthesis rates and induces atrophy, events associated with decreased mitochondrial respiration and increased reactive oxygen species (ROS).
- Since dietary nitrate can improve mitochondrial bioenergetics, this study examined whether nitrate supplementation attenuates disuse-induced impairments in mitochondrial function and muscle protein synthesis rates.
The findings of this meta‐analysis suggest that combined intake of DHA + EPA is likely to lower triglyceride and non-HDL-c, especially when the dose is more than 2 g/day. 

- Evidence of an approximately linear dose–response relationship for triglyceride and non‐HDL‐C reduction among the general population and especially in populations with hyperlipidemia and overweight/obesity was observed.
- These inverse correlations were more prominent in participants receiving basal lipid‐lowering medications or with pre-existing coronary heart disease, given the intake dose was higher than 2 g/d.
In this one, HMB supplementation was associated with improvements in muscle strength, physical performance and muscle quality (defined as the handgrip strength/fat-free mass ratio) in older adults with sarcopenia during a resistance exercise program. 
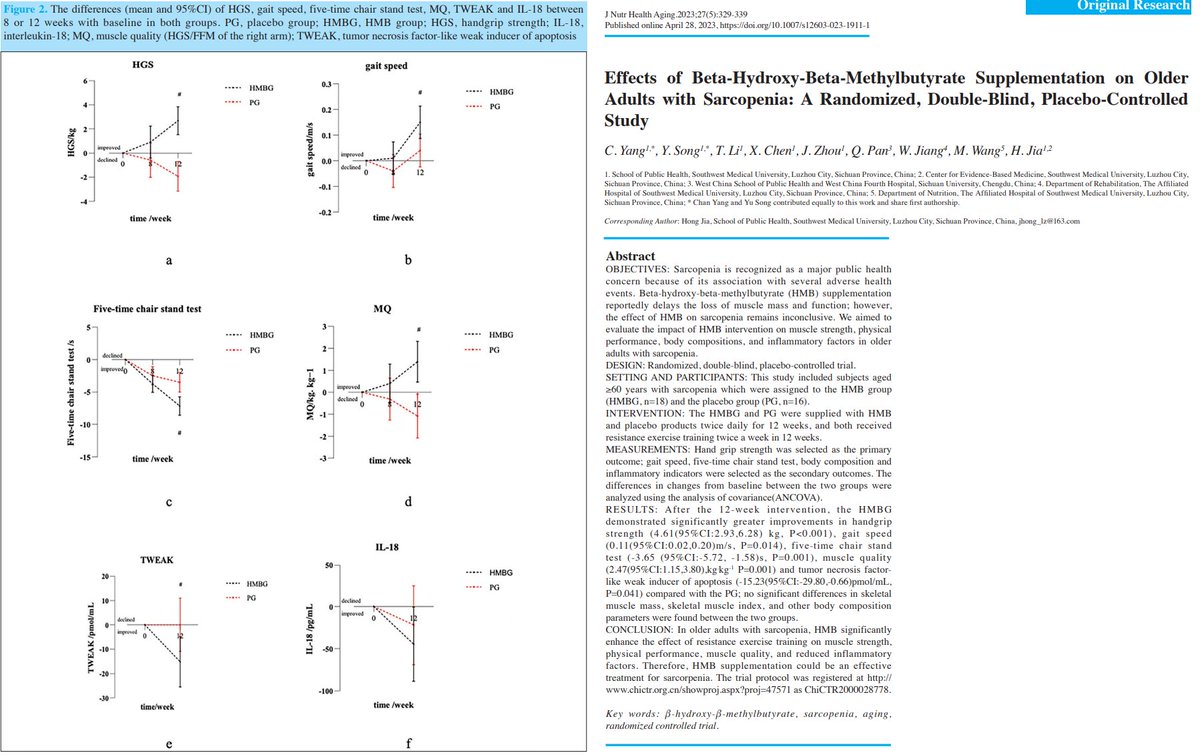
- This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study aimed to evaluate whether HMB supplementation can improve muscle strength, function, and body composition in older adults with sarcopenia.
- This study included subjects aged ≥60 years with sarcopenia which were assigned to the HMB group or the placebo group.
Here, even though both acute and short-term supplementation with nitrate-rich beetroot juice were found to have equally beneficial effects on muscle speed and power in older individuals, no apparent changes in blood pressure or plasma markers of oxidative stress were observed. 

- Sixteen community-dwelling older men and women with a mean age of 71 years completed this registered clinical trial.
- The participants not on the placebo group drank 140 mL of concentrated beetroot juice containing (based on direct measurement) 18.2±6.2 of NO3-.
In this one, ketone ester supplementation was associated with increases in circulating dopamine concentration, and improvements in mental alertness and post-exercise muscular inflammation in ultra-endurance exercise. 

- This study explored the potential of ketone ester intake to elevate systemic dopamine concentrations and psychocognitive functioning in an ultra endurance running event.
- As a secondary aim the study also looked at the effect of exogenous ketosis on muscle repair and recovery of functional capacity following the event.
In this one, 2 years of creatine supplementation during a combined exercise program in postmenopausal women was not associated with improvements in bone mineral density, although some bone geometric properties at the proximal femur were more likely to be preserved. 

- The aim of the study was to examine the effects of 2 years of creatine monohydrate supplementation and exercise on bone health in postmenopausal women.
- Postmenopausal women with a mean age of 59 years were randomized to receive creatine (0.14g/kg) or placebo during a resistance training (3 days/week) and walking (6 days/week) program for 2 years.
In this one, a high dose (2.5mg) of phenylcapsaicin was associated with a plausible ergogenic effect on strength performance, muscle damage and peripheral perceived exertion in comparison to a placebo and a lower dose of 0.625mg during resistance training. 
- The aim of this study was to explore the effects of low dose (0.625 mg) and high dose (2.5mg) of phenylcapsaicin on full squat performance, active muscle and overall body ratings of perceived exertion, muscle damage, protein breakdown, metabolic response, and 24-h recovery.
These assessments were approached under a randomized, triple-blinded, placebo-controlled, crossover design.
Interestingly, findings from this one may suggest that prolonged supplementation with medium and low, but not high, doses of dietary nitrate may have positive effects on blood pressure and endothelial function in older overweight and obese adults. 

- This study used three different doses of NO3- provided for 13-weeks and showed that consumption of the medium and low doses of NO3- (400 mg/day and 400 mg on alternate days) were effective in lowering systolic blood pressure.
- Interestingly, in this study, there was no effect of the high dose of NO3- (800 mg/day) on blood pressure changes.
This narrative review tries to determine the potential impact of dietary Arginine and citrulline supplements, including citrulline malate, on cardiovascular health and exercise performance. 

- "Taken together, the results of studies conducted on both recreational athletes and trained athletes show that supplementing with 0.075 g or 6 g of Arg per kg body weight did not enhance physical performance and perceptual feeling of exercise or increase NO synthesis...
"...In addition, consuming 2.4 to 6 g of Cit per day for 7 to 16 days of various NSs increased NO synthesis, improved athletic performance, and reduced feelings of exertion...
This systematic review and meta-analysis suggests that vegetarians and particularly vegans who live in countries with no current mandatory salt iodisation programme are more likely to have increased risk of low iodine status, iodine deficiency and inadequate iodine intake. 



- Individuals following vegan and vegetarian diets, living in countries without mandatory salt iodisation, and not consuming seaweed or iodine-containing supplements...
...were found to have an increased risk of low iodine status, iodine deficiency, and inadequate iodine intake compared to adults following less restrictive diets living in countries lacking mandatory iodisation of salt.
This review provides an update to the position stand of the International Society of Sports Nutrition (ISSN), integrating current literature on energy drinks and energy shots in exercise, sport, and medicine. 

This is extremely extensive, or should I say exhaustive.
I can only include *some* of the concluding keypoints:
I can only include *some* of the concluding keypoints:
- Energy drinks can enhance acute aerobic exercise performance, largely influenced by the amount of caffeine (> 200 mg or >3 mg∙kg bodyweight [BW−1]) in the beverage.
This systematic review and meta-analysis suggests that beetroot or nitrate supplements are not likely to improves body composition indices regardless of supplement dosage, trial duration, and athletic status.
- All included studies indicated that beetroot or nitrate supplementation are not likely to change body composition indices of the intervened groups compared with controls.
- Subgroup analyses suggested no significant differences in body composition-related outcomes between subgroups in terms of duration of intervention, dose, study design, baseline BMI of participants, and athletic status (athlete versus non athlete).
This systematic review and meta-analysis comes to the conclusion that n-3 PUFA supplementation is likely to lead to very small increases in muscle strength, but it is not likely to confer an impact in muscle mass and function in healthy adults (young and older).
- "Our results are in contrast with the meta-analysis published by Huang et al, who found minor increases in muscle mass and function in the elderly after n-3 PUFA supplementation...
Ref:
doi.org/10.3390/nu1212…
Ref:
doi.org/10.3390/nu1212…
"...The fact that they included measurements of muscle mass based on DXA, bioelectrical impedance analysis, and computed tomography, while we only considered gold-standard measurements... may help to explain the discrepancy between our findings...
This systematic review and meta-analysis suggests that CoQ10 supplementation is likely to improve lipid profiles in adults, with the optimal dose being 400-500mg/day. 

- CoQ10 supplementation is likely to decrease total cholesterol, LDL-c, and TG and increase HDL-c levels in the adult population.
- Dose–response analysis revealed an inverse J-shaped nonlinear pattern between CoQ10 supplementation and TC, in which the optimal dose was 400 to 500 mg/day.
#1 #Covid19 #Supplement thread for #LongCovid #LongHaul #PostCovid. This may help, if you suffer from #fatigue #brainfog #jointpain #inflammation #weakness #depression #anxiety #SOB #clots #fibrosis #myocarditis #heartattack #stroke #alz #memory frontiersin.org/articles/10.33…
#2 B-COMPLEX/MULTI VITAMIN. Buy a liposomal or other form that increases bio-availability. Take 1 capsule w/Breakfast and Lunch. If you have stomach upset, try sublingual (under tongue) EZ Melt B-Complex in AM & Multi w/iron for Dinner. amazon.com/Liposomal-Meth…
#3 OMEGA 3s. Fish Oil, Krill Oil, Algae Oil are all good sources of Omega 3. Be careful the EPA/DHA ratio. EPA helps with inflammation/DHA helps with cognition. You need both! Opt for a 1:1 or 2:1 ratio of DHA to EPA (2:1 ratio eg. 800 DHA/400EPA) amazon.com/3Care-Concentr…
1
Ok this is interesting #livertwitter #MedTwitter
26 yr old woman with jaundice+severe itching (a.k.a cholestatic hepatitis). Routine causes - viruses, prescription drugs, autoimmune liver disease blood tests - neg. No #ayurveda or #herbal drug use. Mysterious🤔
Liver biopsy👇
Ok this is interesting #livertwitter #MedTwitter
26 yr old woman with jaundice+severe itching (a.k.a cholestatic hepatitis). Routine causes - viruses, prescription drugs, autoimmune liver disease blood tests - neg. No #ayurveda or #herbal drug use. Mysterious🤔
Liver biopsy👇

2
#pathology expert says its #drug induced liver injury. But patient denies any drug use. She has #PCOD - polycystic ovarian disease (mayocl.in/34S2LMh) and hence, #overweight.
Deep dive into history again - says she's taking #vitamins for weight loss! Asked to show👇
#pathology expert says its #drug induced liver injury. But patient denies any drug use. She has #PCOD - polycystic ovarian disease (mayocl.in/34S2LMh) and hence, #overweight.
Deep dive into history again - says she's taking #vitamins for weight loss! Asked to show👇

3
Can you identify the culprit component that caused this woman's severe liver injury? #Pathologist is right! #PathTwitter
Culprit - Chromium picolinate in #health #supplement 4 #diabetes #weigthloss. #Chromium is micronutrient enuf in daily food intake bit.ly/3nYNeBB
Can you identify the culprit component that caused this woman's severe liver injury? #Pathologist is right! #PathTwitter
Culprit - Chromium picolinate in #health #supplement 4 #diabetes #weigthloss. #Chromium is micronutrient enuf in daily food intake bit.ly/3nYNeBB

So disappointing to see #immuneboost bunk pushed during a pandemic.
"How to naturally boost your immune system" globalnews.ca/news/7486294/i… via @Globaltv @morningshowCA @jmacspeaks HT @DanielJDrucker
Eating healthy great, but science to support many of these claims iffy at best...
"How to naturally boost your immune system" globalnews.ca/news/7486294/i… via @Globaltv @morningshowCA @jmacspeaks HT @DanielJDrucker
Eating healthy great, but science to support many of these claims iffy at best...
Inaccurate immune boost nonsense circulating everywhere.
Our recent studies found 85.5% of websites provide inaccurate boost bunk: bmjopen.bmj.com/content/10/10/… cc @morningshowCA @carolynglobal
Instagram immune boost posts usually "devoid of sound science" aacijournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.11…
Our recent studies found 85.5% of websites provide inaccurate boost bunk: bmjopen.bmj.com/content/10/10/… cc @morningshowCA @carolynglobal
Instagram immune boost posts usually "devoid of sound science" aacijournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.11…
And enough with the "Vitamin D" hype! There is, for sure, interesting science on point. It is a space we should watch. But much of the research is observational.
See this helpful critique in context of #COVID conscienhealth.org/2020/11/seriou… by @ConscienHealth cc @liz272 @morningshowca
See this helpful critique in context of #COVID conscienhealth.org/2020/11/seriou… by @ConscienHealth cc @liz272 @morningshowca
1. I have compiled a collection of online supplements-in-bulk retailers since @BulkSupps doesn't seem that interested in fixing the bugs on their website. They seem to be moving to a mobile-device-only store - I don't do phone stuff, ever, like most researchers.
2. Here are some sites that compiled online #supplement store competitors:
sitelike.org/similar/bulksu…
sitelike.org/similar/bulksu…
